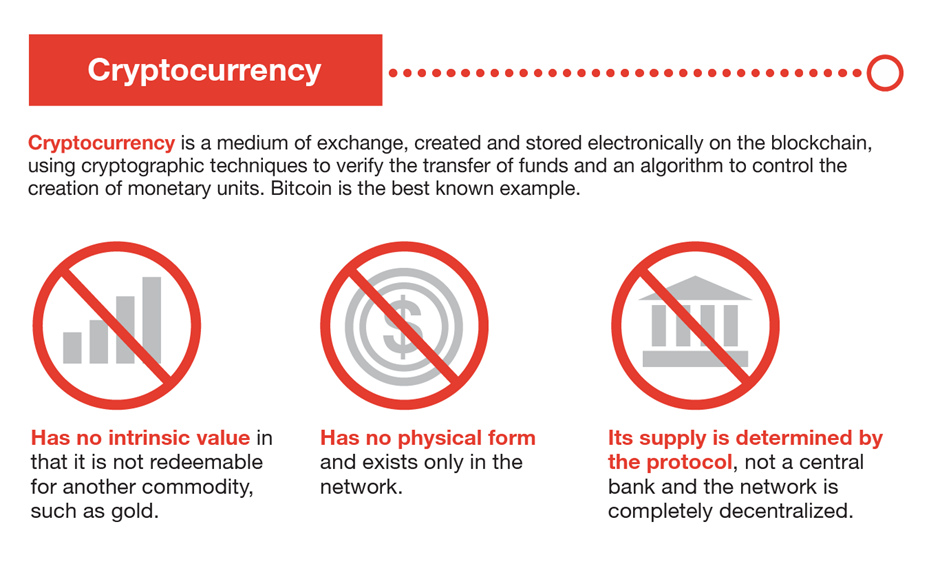
Let’s begin by quickly defining some terms. The technology that makes bitcoin possible is called blockchain. (among other things). Bitcoin is the name of the best-known cryptocurrency, the one for which blockchain technology, as we presently know it, was created. A cryptocurrency is a form of digital currency similar to the US dollar that controls the creation of new units of currency and uses cryptographic techniques to validate the transfer of funds.
What is blockchain technology?
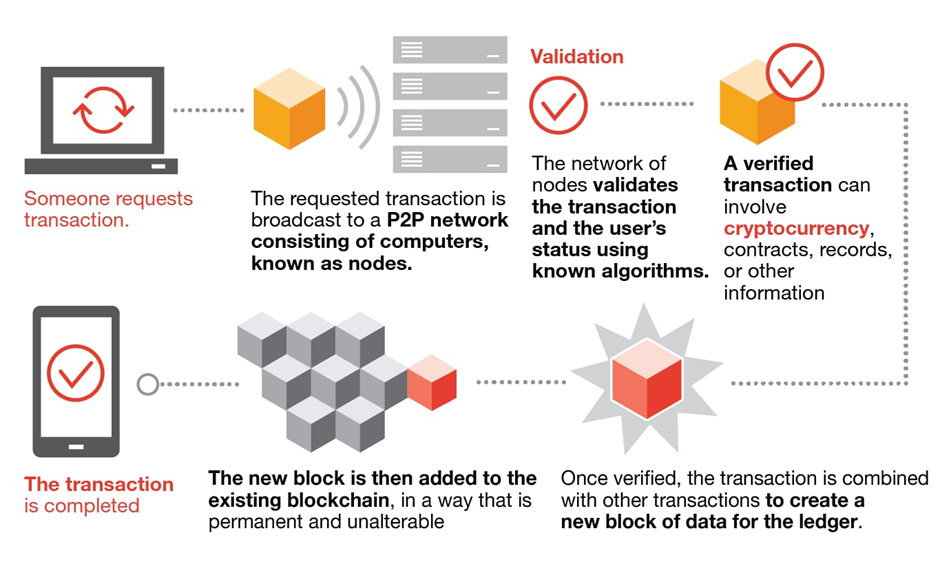
A peer-to-peer network’s entire activities are recorded in a blockchain, which is a decentralized ledger. Participants can validate transactions using this technology without the need for a central clearing organization. Applications might involve paying bills, concluding business deals, casting ballots, and a host of other things.
What is cryptocurrency?
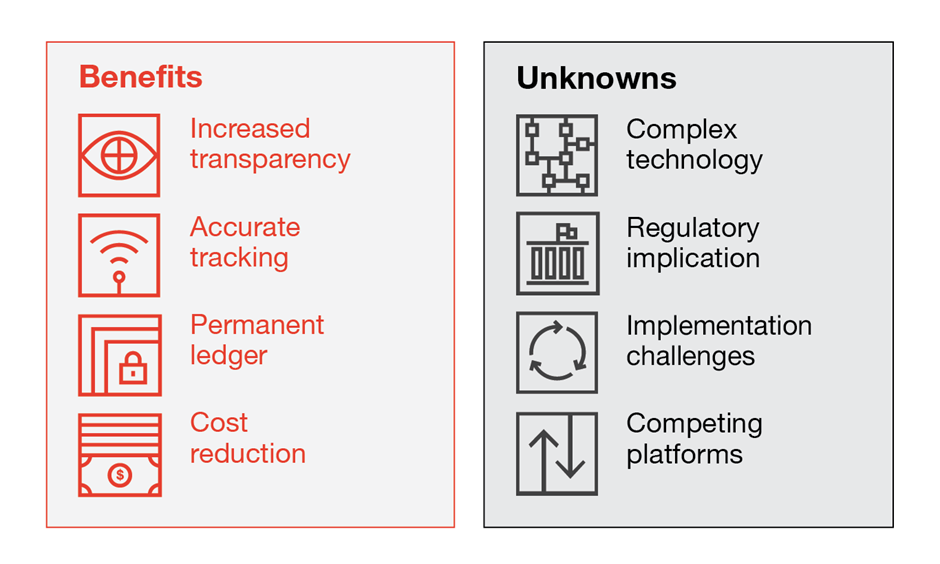
Blockchain’s benefits and unknowns
How blockchain works
Blockchain’s potential applications
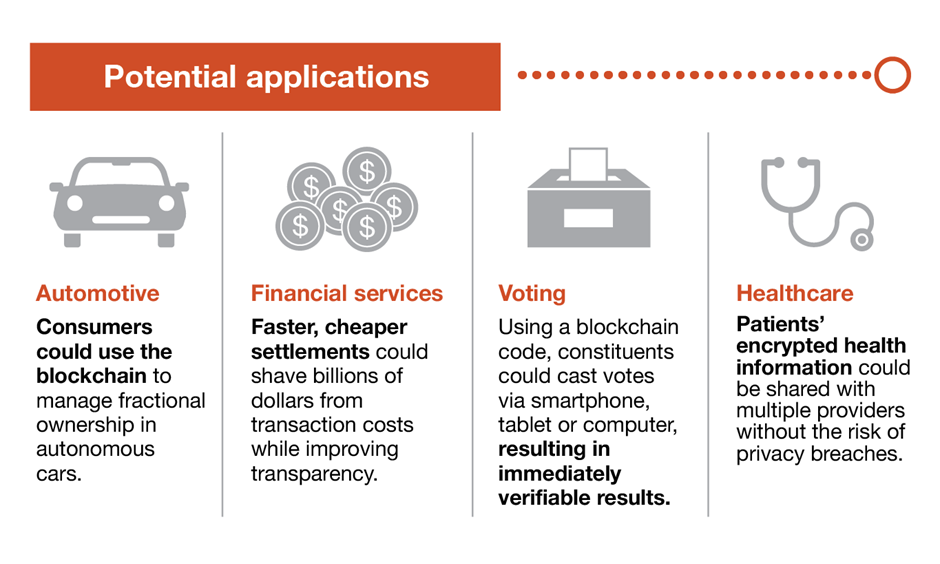
Blockchain also has potential applications far beyond bitcoin and cryptocurrency.
It’s useful to think of blockchain technology as a new breed of business process improvement software from a commercial standpoint. Blockchain and other collaborative technologies promise to significantly reduce the “cost of trust” by enhancing the business processes that take place between businesses. Because of this, it might provide considerably higher returns for every dollar invested than the majority of conventional internal investments.
Financial organizations are looking into how blockchain technology could revolutionize everything from insurance to clearing and settlement. These articles will aid in your comprehension of these shifts as well as your next steps.
Start with this for an introduction to cryptocurrencies: Money is not an issue. We examine bitcoin’s early history and present poll data on consumer familiarity, usage, and other topics. We also consider how market players, including financiers, technology suppliers, and investors, will be impacted as the market develops.
We advise reading the following to learn more about cryptocurrencies:
PwC’s open information repository on all things crypto is called the Crypto Center. A summary of authorities’ perspectives on cryptocurrencies in financial services, both domestically and internationally, can be found in Carving Up Crypto. Cryptocurrency? digital resource? How are the accounts? We go over the definitions of these words and how they affect your financial statements in this podcast.
Board members should: Ten cryptocurrency-related questions that every board should ask offer ideas for topics to discuss when discussing the strategic potential of cryptocurrencies.
For a summary of blockchain technology in the financial industries. We look at some of the blockchain applications used by FS companies and discuss how we anticipate the technology to advance moving forward. Although blockchain isn’t a panacea, there are undoubtedly many issues for which this technology is the best option.
We suggest: A strategist’s guide to blockchain, which examines the potential advantages of this significant innovation and offers advice for financial institutions on how to move forward. For a deeper dive on particular subjects related to blockchain. Examine how blockchain technology might be used by competitors to harm your business and how your business might use it to advance.
Fundamental elements: This article explores some of the concerns that internal audit and other parties might have with a blockchain solution and how you can start to allay some of them. It also discusses how financial services can build confidence in blockchain.
Even though they happen less frequently and with less fanfare now than they did a few years ago, blockchain statements still take place. However, the financial services sector could experience a fundamentally different competitive future as a consequence of blockchain technology.



